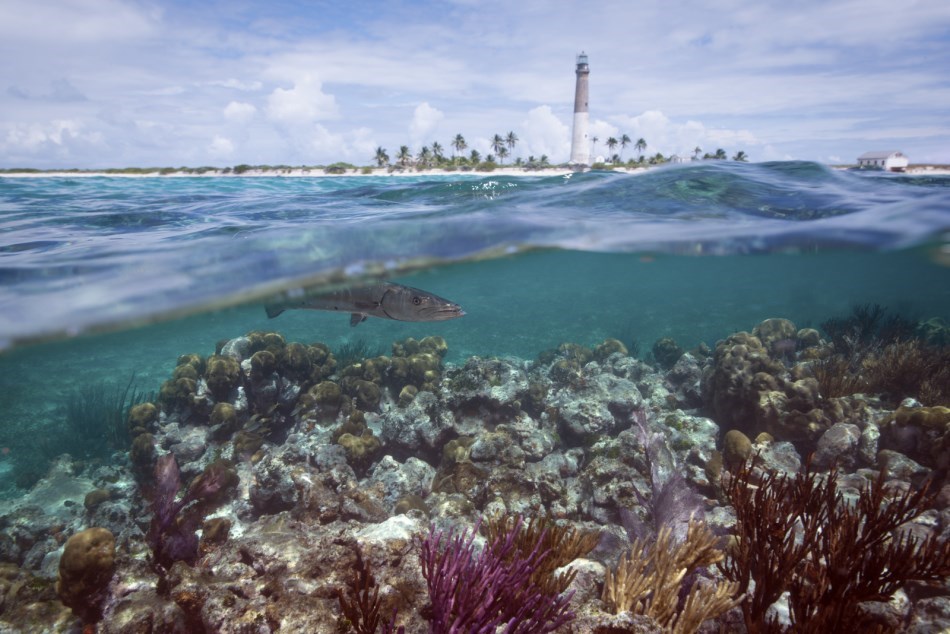
It is the third largest coral barrier reef system in the world (after the Great Barrier Reef and Belize Barrier Reef). It lies a few miles seaward of the Florida Keys, is about 4 miles (6 to 7 km) wide and extends (along the 20 meter depth contour) 270 km (170 mi) from Fowey Rocks just east of Soldier Key to just south of the Marquesas Keys. The barrier reef tract forms a great arc, concentric with the Florida Keys, with the northern end, in Biscayne National Park, oriented north-south and the western end, south of the Marquesas Keys, oriented east-west.
The rest of the reef outside Biscayne National Park lies within John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park and the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Isolated coral patch reefs occur northward from Biscayne National Park as far as Stuart, in Martin County. Coral reefs are also found in Dry Tortugas National Park west of the Marquesas Keys. There are more than 6,000 individual reefs in the system. The reefs are 5,000 to 7,000 years old, having developed since sea levels rose following the Wisconsinan glaciation.

The Florida Reef consists of two ridges separated from the Florida Keys by the Hawk Channel. Closest to the Keys is a sand ridge called White Bank, covered by large beds of sea grass, with patch reefs scattered across it. Further out to sea on the edge of the Florida Straits is the second ridge forming the outer reefs, covered by reefs and hard banks composed of coral rubble and sand.
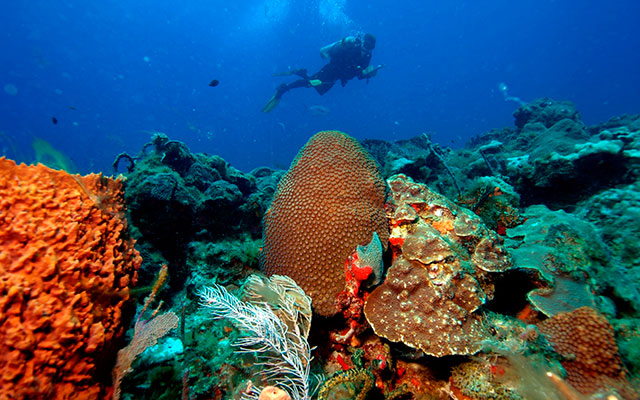

Almost 1,400 species of marine plants and animals, including more than 40 species of stony corals and 500 species of fish, live on the Florida Reef. The Florida Reef lies close to the northern limit for tropical corals, but the species diversity on the reef is comparable to that of reef systems in the Caribbean Sea.

According to wikipedia








